Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing cybersecurity, offering advanced tools to combat increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. From detecting malware in real time to predicting zero-day vulnerabilities, AI and cybersecurity are reshaping how organizations defend their digital assets. This 3000-word guide explores the role of AI in cybersecurity, its applications, risks, and future trends, while addressing critical questions like “Will AI replace cybersecurity jobs?” and “How can AI be used in cyber security?”
1. Introduction to AI and Cybersecurity
What is cybersecurity and its importance?
Cybersecurity involves protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. With cybercrime costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 (Cybersecurity Ventures), integrating AI and cybersecurity has become critical for:
- Real-time threat detection: Identifying malware, phishing, and ransomware.
- Automated response: Neutralizing attacks before they escalate.
- Predictive analytics: Forecasting vulnerabilities using historical data.
AI and cybersecurity work symbiotically: AI enhances defense mechanisms, while cybersecurity frameworks ensure AI systems themselves remain secure.
2. How AI is Used in Cybersecurity
Key Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
- Threat Detection and Prevention:
- Machine learning (ML) algorithms analyze network traffic to flag anomalies.
- Example: Darktrace’s Enterprise Immune System detects novel threats.
- Phishing Detection:
- NLP models scan emails for suspicious language (e.g., urgent payment requests).
- Vulnerability Management:
- AI tools like Tenable.io prioritize patches based on exploit likelihood.
- Identity Verification:
- Biometric authentication (e.g., facial recognition) replaces passwords.
- Incident Response:
- Automated playbooks isolate infected devices and restore backups.
AI in Cybersecurity Workflow
1️⃣ Data Collection from Multiple Sources
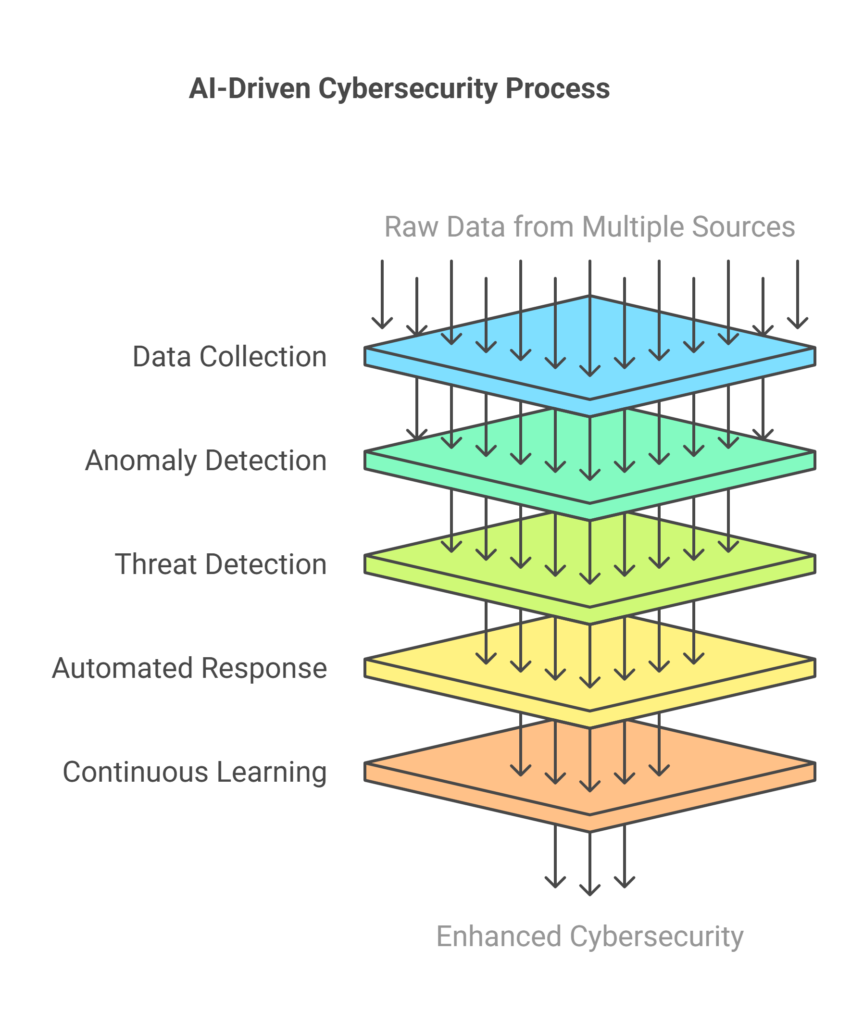
AI gathers data from various endpoints, including:
✔ Devices & Endpoints – Computers, mobile devices, IoT gadgets
✔ Network Traffic – Packets, logs, DNS requests
✔ Cloud Systems – SaaS applications, cloud storage
✔ User Behavior – Login patterns, access controls
2️⃣ Data Processing & Anomaly Detection
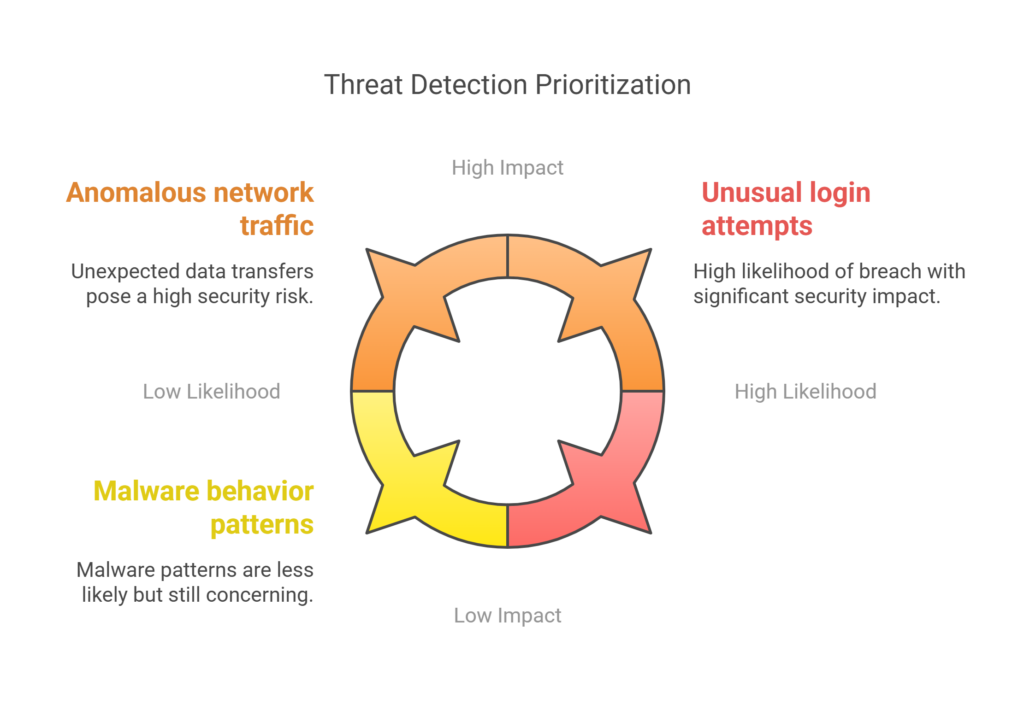
🔍 AI analyzes massive volumes of security logs in real-time, identifying unusual activities such as:
✔ Unusual login attempts (e.g., login from a new location or device)
✔ Anomalous network traffic (e.g., unexpected data transfers)
✔ Malware behavior patterns (e.g., file execution anomalies)
Machine learning models compare normal vs. suspicious behavior using historical data to flag potential threats before they escalate.
3️⃣ Threat Detection & Risk Scoring
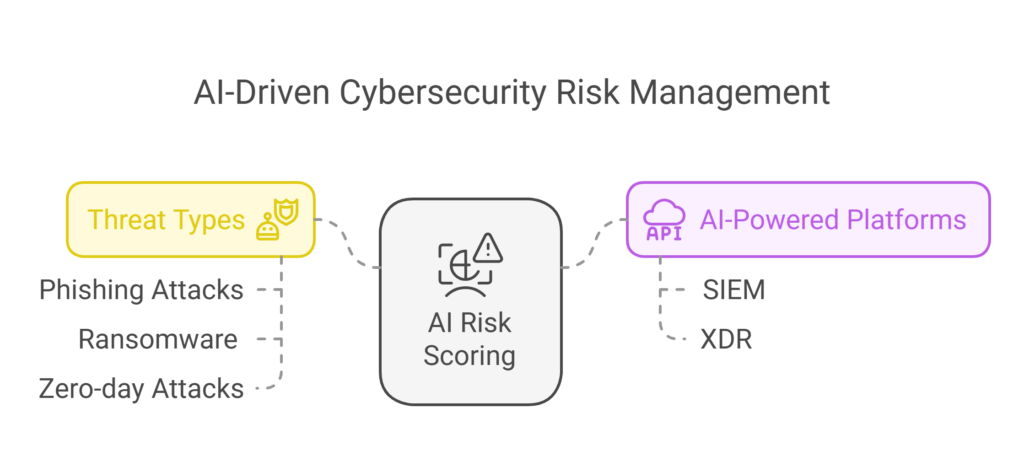
🔹 AI assigns risk scores based on detected threats.
🔹 Higher scores indicate immediate cybersecurity risks, such as:
✔ Phishing attacks – Email-based deception attempts
✔ Ransomware – Encrypted files demanding a ransom
✔ Zero-day attacks – Newly discovered vulnerabilities
AI-powered Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platforms help security teams prioritize alerts efficiently.
4️⃣ Automated Threat Response & Mitigation
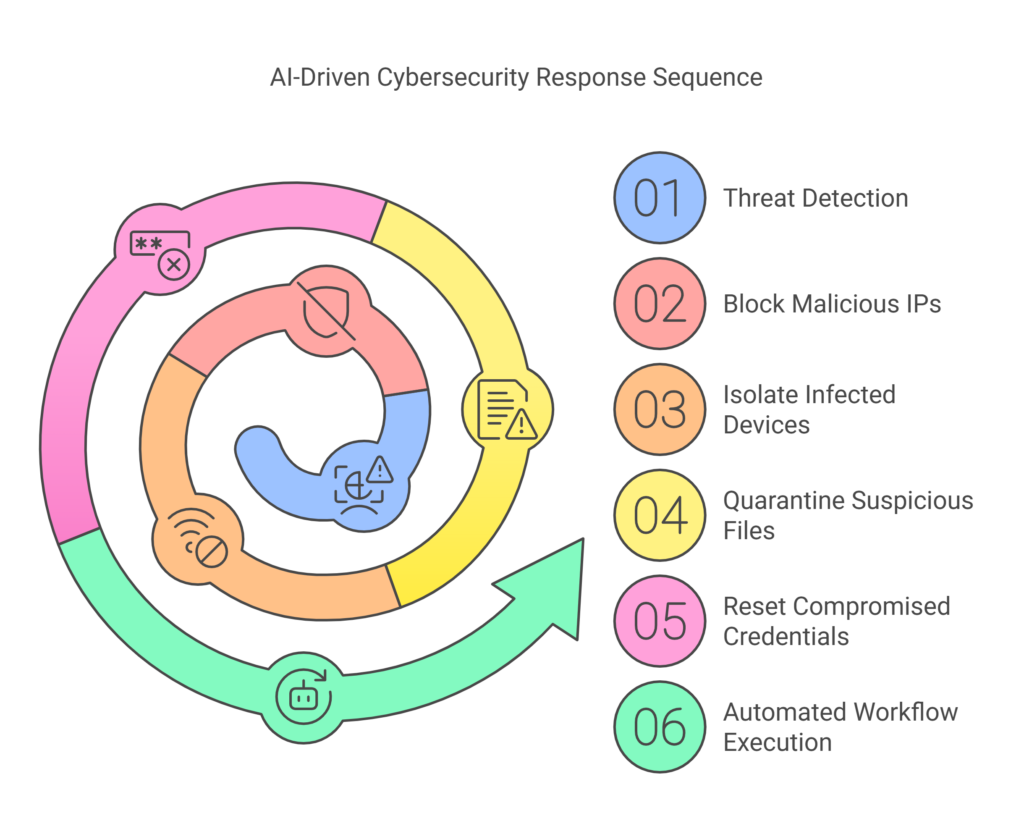
🚀 Once a threat is detected, AI takes instant action to prevent cyberattacks, including:
✔ Blocking malicious IPs and restricting network access
✔ Isolating infected devices from the network
✔ Quarantining suspicious files to prevent further execution
✔ Resetting compromised credentials to prevent unauthorized access
AI-driven Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) systems automate workflows, reducing response time from hours to seconds.
5️⃣ Continuous Learning & Adaptation
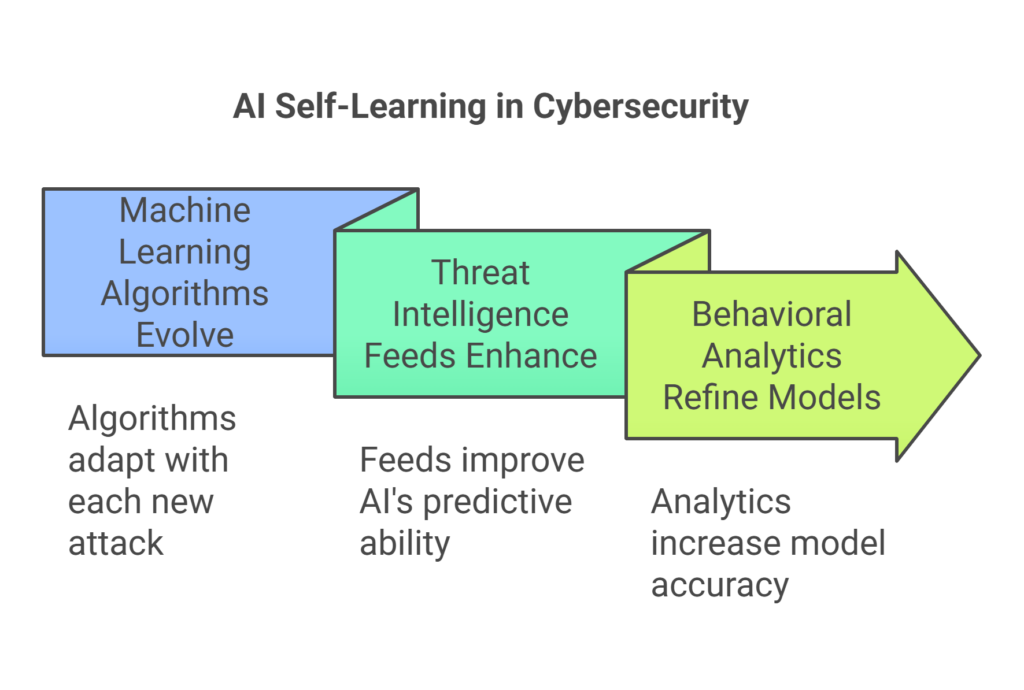
💡 AI in cybersecurity is self-learning and improves over time:
✔ Machine learning algorithms evolve with every new attack
✔ Threat intelligence feeds enhance AI’s ability to predict attacks
✔ Behavioral analytics refine security models for better accuracy
Cybersecurity AI continuously adapts to new attack techniques, ensuring proactive defense against ever-evolving cyber threats.
How AI Helps in Cyber Security
- Speed: Processes petabytes of data in seconds.
- Accuracy: Reduces false positives by 80% (IBM).
- Scalability: Protects IoT devices, cloud infrastructure, and remote workforces.
3. AI vs Cybersecurity: Key Differences
| Aspect | AI | Cybersecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Creating intelligent systems. | Protecting systems from threats. |
| Tools | ML, neural networks, generative AI. | Firewalls, encryption, penetration testing. |
| Goal | Automate tasks, predict outcomes. | Ensure confidentiality, integrity, availability (CIA triad). |
Is cybersecurity better than artificial intelligence?
No—they are complementary. AI enhances cybersecurity efficacy, while cybersecurity safeguards AI systems from adversarial attacks.
4. Generative AI and Cybersecurity: Opportunities and Risks
Generative AI (Gen AI)—models like ChatGPT and DALL-E—introduces transformative possibilities and challenges:
Opportunities
- Threat Simulation: Mimic attacks to test defenses (e.g., phishing email generation).
- Code Auditing: Detect vulnerabilities in software using tools like GitHub Copilot.
Risks
- AI-Generated Attacks: Hackers create polymorphic malware that evades detection.
- Deepfakes: Synthetic media bypasses biometric checks.
Case Study: In 2023, a deepfake audio scam impersonated a CEO, tricking a firm into transferring $35 million.
5. AI and ML in Cybersecurity: Tools and Technologies
Leading AI-Based Cybersecurity Tools
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Uses ML to detect endpoint threats.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: Correlates data across networks for faster response.
- IBM QRadar: Analyzes logs with AI to identify suspicious patterns.
AI and Cybersecurity Course Recommendations
- Free Courses:
- Google Cybersecurity Certificate (Coursera).
- MIT OpenCourseWare: AI for Cybersecurity.
- Paid Certifications:
- Certified AI Security Engineer (CAISE) ($1,200).
- SANS SEC595: Machine Learning for Cybersecurity ($8,000).
6. Disadvantages of AI in Cybersecurity
Key Challenges
- Adversarial Attacks: Hackers manipulate AI models with poisoned data.
- Bias: Flawed training data leads to incorrect threat classifications.
- High Costs: Implementing AI requires investment in infrastructure and talent.
- Over-Reliance: Organizations may neglect human expertise.
Example: In 2022, an adversarial attack tricked an AI system into misclassifying malware as benign.
7. The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
Emerging Trends
Autonomous Security Systems: AI-driven systems that self-patch vulnerabilities.
Quantum AI: Encrypts data using quantum-resistant algorithms.
AI-Powered Threat Hunting: Proactively identifies advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Prediction: By 2030, 50% of cybersecurity tools will leverage AI (Gartner).
8. AI and Cybersecurity Jobs: Will AI Replace Humans?
Will AI Replace Cybersecurity Jobs?
No—AI will augment roles rather than replace them. The future of cyber security jobs will prioritize:
- AI Security Analysts: Auditing AI models for vulnerabilities.
- Threat Hunters: Investigating AI-flagged anomalies.
- Ethical Hackers: Pen-testing AI systems.
Projection: Cybersecurity jobs will grow by 35% from 2021–2031 (BLS).
9. How to Learn AI and Cybersecurity: Courses and Certifications
Cyber Security and AI Course Pathways
- Beginner:
- Cybersecurity Fundamentals (IBM).
- AI For Everyone (Andrew Ng, Coursera).
- Advanced:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): Focuses on AI-driven penetration testing.
- Machine Learning Engineering for Production (MLOps) (DeepLearning.AI).
AI and Cybersecurity Infographic

10. FAQs About AI and Cybersecurity
Q1: How can AI help in cyber security?
A: AI detects threats faster, automates responses, and predicts vulnerabilities using ML.
Q2: Will AI take over cyber security?
A: No—AI enhances human capabilities but cannot replace critical thinking or ethical judgment.
Q3: What is the difference between AI and cyber security?
A: AI builds intelligent systems, while cybersecurity protects digital assets. They work together to improve defense mechanisms.
Q4: Is cyber security better than AI?
A: They serve different purposes. Cybersecurity is a field; AI is a tool used within it.
Q5: What is cybersecurity and ethical hacking?
A: Ethical hacking involves legally penetrating systems to find flaws, a subset of cybersecurity.
11. References
IBM Report: Cost of a Data Breach 2023.
Gartner: Future of AI in Cybersecurity.
Coursera: Google Cybersecurity Certificate.
MIT OpenCourseWare: AI for Cybersecurity.












Leave a Reply